


Jian Ye's team successfully used a deep neural network model to predict the optical properties of nanomaterials
September 07, 2019
On August 26, 2019, The research group of Jian Ye, School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, published “Plasmonic Nanoparticle Optical Simulation and Inverse Prediction Using Machine Learning” on Nano Scale.
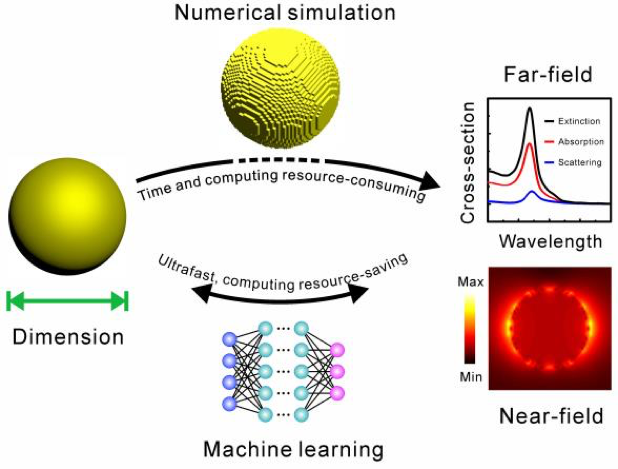
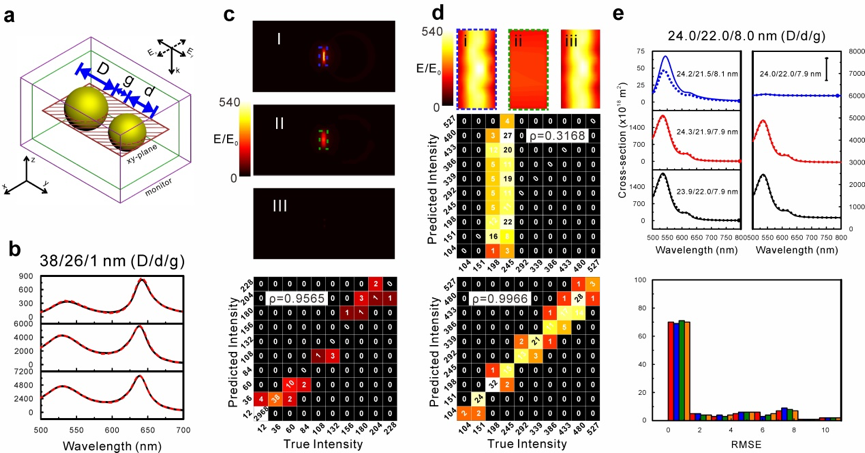
Collective oscillation of quasi-free electrons on the surface of metallic plasmonic nanoparticles (NPs) in the ultraviolet to near-infrared (NIR) region induces a strong electromagnetic enhancement around the NPs, which leads to numerous important applications. These interesting far- and near-field optical characteristics of the plasmonic NPs can be typically obtained from numerical simulations for theoretical guidance of NP design. However, traditional numerical simulations encounter irreconcilable conflicts between the accuracy and speed due to the high demand of computing power. In this work, we utilized the machine learning method, specifically the deep neural network (DNN), to establish mapping between the far-field spectra/near-field distribution and dimensional parameters of three types of plasmonic NPs including nanospheres, nanorods, and dimers. After the training process, both the forward prediction of far-field optical properties and the inverse prediction of on-demand dimensional parameters of NPs can be accomplished accurately and efficiently with the DNN. More importantly, we have achieved for the first time ultrafast and accurate prediction of two-dimensional on-resonance electromagnetic enhancement distributions around NPs by greatly reducing the amount of electromagnetic data via screening and resampling methods. These near-field predictions can be realized typically in less than 10(-2) seconds on a laptop, which is 6 orders faster than typical numerical simulations implemented on a server. Therefore, we demonstrate that the DNN is an ultrafast, highly efficient, and computing resource-saving tool to investigate the far- and near-field optical properties of plasmonic NPs, especially for a number of important nano-optical applications such as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, photocatalysis, solar cells, and metamaterials.
This study was conducted by Jian Ye's research group, the School of Biomedical and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. PhD students Jing He and Chang He are co-first authors, and Professor Jian Ye is the corresponding author. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and the Shanghai Key Laboratory of Gynecologic Oncology, Guangci Professorship Program of Ruijin Hospital.